TEl: +86-13148388090
Fax:+86-571-88616515
Nursing Care Plan for Urinary Tract Infections
Author: admin / 2024-08-05What is a urinary tract infection?
If the urethra, bladder, and kidneys are infected by pathogens such as Escherichia coli you get urinary tract infections (UTIs). This article explores the diagnosis and treatment of the infection and discusses nursing care plans for urinary tract infections.
When your kidneys remove waste and excess water from your blood urine is produced. Urine enters the bladder through narrow tubes from the kidneys. These tubes are called ureters. The bladder stores urine until it is time to urinate. Urine is removed from the body through the urethra. Sometimes bacteria get into your urinary system and cause UTIs.
Besides Escherichia coli, which is the main pathogen causing UTIs, other common microbial organisms responsible for the disease are Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Enterococcus spp. It is important to note that indwelling catheters, especially if used for extended periods, is a common risk factor for UTIs.
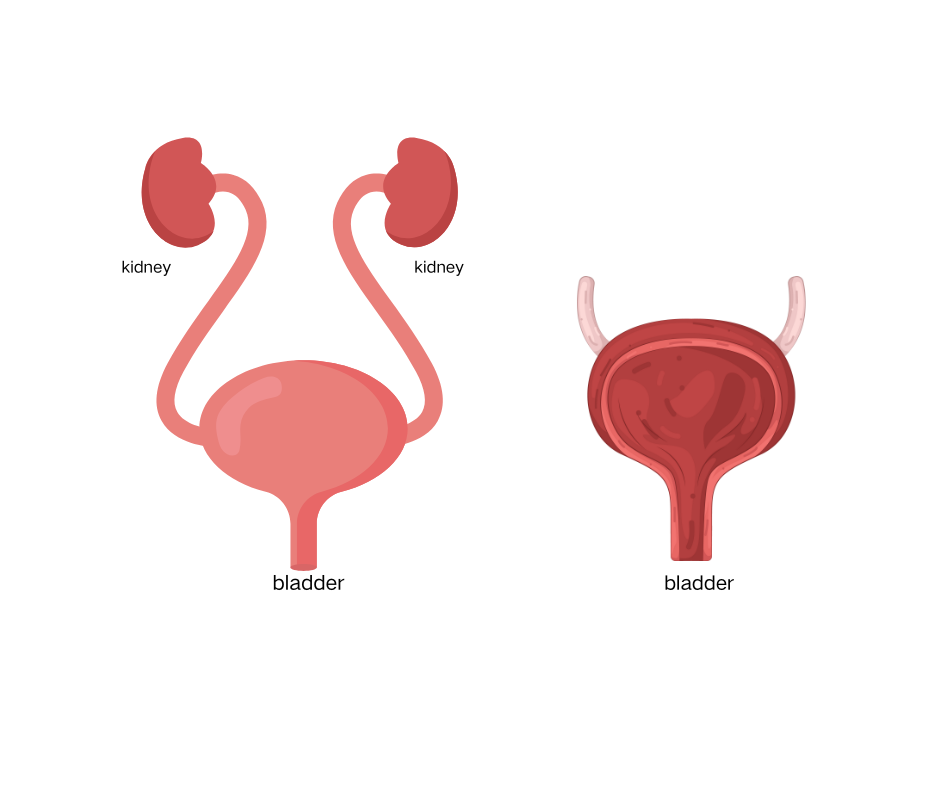
Structure of the urinary tract
The urinary tract includes the following parts:
a. Kidneys. Your two kidneys (bean-shaped organs) are located on the back of your body, above your hips. They filter water and waste products from your blood, this is how urine is produced. Common wastes include urea and creatinine.
b. Ureters. Urine comes from your kidneys to the bladder through ureters (they are basically thin tubes).
c. Bladder. The bladder stores urine before it exits your body.
d. Urethra. The urethra is a tube that carries pee from your bladder to the outside of your body.
Symptoms of urinary tract infection
Due to the inflammation in the lining of your urinary tract caused by a UTI, you may experience the following:
a. Pain in your flank, abdomen, pelvic area, or lower back.
b. Pressure in the lower part of your pelvis.
c. Urine that looks cloudy and smells bad.
d. Urinary incontinence.
e. Frequent urination.
f. Urge incontinence (an urgent, uncontrollable need to pee several times during the day and night)
g. Pain when you pee (dysuria)
h. Blood in your pee (hematuria).
There may be other UTI-associated symptoms such as pain in your penis, fatigue feeling, fever, chills, pain during sex, and nausea and vomiting.
Causes of urinary tract infection
Urinary tract infections are caused by bacteria (E. coli is the main bacterium causing UTIs). The bacteria can travel through the urethra to infect the bladder. The bacteria may also infect your kidney by coming into your kidney from the bladder through the ureters.
1) E. coli typically exist in your lower intestines (large intestine); for this reason, the anus has a lot of E. coli bacteria. So you should be careful when you go to the toilet lest the bacterium infect your urinary tract.
2) You should also pay attention to your finger hygiene because bacteria on your fingers may have an opportunity to infect your urinary tract.
3) Catheter use.
Catheter use is a risk factor for UTIs. The catheter is a useful medical device for providing continence care to people who cannot urinate on their own, who cannot control urination due to neurological problems, or who are paralyzed. Therefore it is very important the catheters used are of medical grade, have been approved by authorities as suitable for medical use, and are sterile. For a description of high-quality catheters so that you are more informed as to what catheters to use you can refer to information sources such as this website: www.bevermedical.com
Diagnosis of urinary tract infection
If you have symptoms of UTI, talk to your doctor, who may conduct the following tests to confirm the infection.
1) Urinalysis. Your urine sample will be examined in a lab using variables such as nitrites, leukocyte esterase and white blood cells.
2) Urine culture. This technique is used to grow and identify any bacteria that are present in your urine sample.
If your infection does not respond to treatment, it is possible that your urinary tract has a disease that can be detect by the following examinations:
a. Ultrasound. This technology enables the doctor to see an image of your internal organs for diagnosis purposes.
b. Computed tomography (CT) scan. A CT scan takes cross-section images of your body.
c. Cystoscopy. During this test, a cystoscope is used to look inside your bladder through your urethra.
Nursing care plan for urinary tract infection
For a person challenged with the problem of urinary tract infections, the nursing care plan implemented by the healthcare provider usually includes the following:
1) Relieving the pain brought about by the infection.
When you have a UTI, you are faced with a burning or painful sensation during urination. To address this, your healthcare provider will use a combination of pain medicines, heat therapy, hydration, and antibiotics.
Your doctor will prescribe an antibiotic that is targeted at the specific bacteria that cause your infection. The antibiotics used for UTIS include Nitrofurantoin, Sulfonamides, Amoxicillin, Cephalosporins, Doxycycline, and Fosfomycin, Quinolones.
2) UTI patients'complaints may include dysuria, urinary frequency, and urgency. Therefore you will be helped with urinary elimination which significantly improves your quality of life.
3) Administering Medications
Your healthcare provider prescribes antibiotics based on the specific bacteria causing the infection and relevant resistance patterns.
4) You may also be instructed on how to prevent a urinary tract infection.
A. Hygiene is important
In the case of a woman, it is recommended to wipe from front to back after pooping to avoid bacteria getting into the urethra. Also, you should replace your sanitary pads regularly.
B. Drink plenty of water. Six to eight glasses of water daily is recommended, because this helps flush out bacteria from your urinary tract.
C. Pee is a waste product, so if you pee frequently you remove waste from your body often, which reduces the chance of developing a urinary tract infection. Also, remember to pee before and after having sex.
D. In order to prevent moisture from accumulating around your urethra, loose-fitting clothing and cotton underwear are recommended.
Urinary tract infections cause inconvenience and sometimes incontinence. There is no adult who is immune from this disease, and it should be treated right away in order to avoid complications.


